For a long time, getting an ultra-fast internet connection meant using a wired connection. However, there are huge advancements in wireless communications such that users can access internet speeds closer to wired connections. 5G is the embodiment of the advancements.
What is 5G connection?
Connectivity to the internet via mobile devices has come a long way. Initially, connections like Enhanced Data GSM Environment (EDGE) could allow a few bursts of data to be relayed via broadband techniques. Only few data could be transferred at speeds not exceeding 384 kilobytes per second.
EDGE is oftentimes referred to as the second generation or 2G broadband connection. With time, the connections have been advanced through stages until the fourth generation or 4G. Compared to the previous connections, 4G is super-fast. But this is not enough to ensure a seamless connection without latency.
Fifth generation or 5G is the answer to the questions which 4G left unanswered. Basically, 5G is super-fast and mobile devices can communicate more reliably than ever before. This kind of connection enables new technologies like machine-to-machine (M2M) communications or Internet of Things (IoT) to operate at near optimum.
Features of 5G
5G is already a buzzword in the technology circles. In fact, this phenomenon is huge to the extent that there is a political storm around it. Here are some features of the connection:
- Estimated travel rate for data is close to 20 gigabytes per second.
- Around 1-millisecond latency hence supporting real-time communication
- Ability to slice networks such that operators can vend 5G-as-a-service
- Increased bandwidth usage per unit area
- Compared to advanced 4G, a 5G connection supports 100 more devices per unit area
Already, a myriad of use cases for 5G is coming up. However, the most crucial will be the ability to enable the rolling out of major IoT technologies in a seamless manner. This includes the ability of self-driving vehicles to navigate their way in the environment successfully.
5G in Canada
Obviously, the immense potential of this technology to revolutionize communications and to expedite the rollout of novel technologies is an opportunity few countries can pass up. Although the rollout of the new mobile wireless connection has been slow in moving, one cannot help but notice steps towards a 5G connected universe.
Canada is among the countries with concrete plans towards the rollout of 5G. Various companies are laying out the groundwork to ensure that the network goes live by 2021. Nonetheless, Canada remains behind countries like China which are blazing the trail in this new niche.
- Major players in Canada’s 5G ambitions
While China and other countries like Canada’s southern neighbor are steps ahead when it comes to 5G, most of the world is still in the dark. In China, and pretty much around the world, Huawei is the main crusader for 5G adoption. The company is also leading some 5G campaigns in Canada but there seems to be a lot of controversy surrounding the campaign.
That leaves Nokia and Ericsson as the major players. These are companies which are working to lay the foundation for the national rollout of the network. However, the major challenge is that most of the hardware necessary for this launch is developed by Huawei. This makes the Chinese tech giant a major player, one way or another, in Canada’s race to 5G.
- Where is Canada in the race toward 5G?
To be sure, most of Canada is currently connected via 4G networks. One of the major challenges for 4G technology is that there is a possibility for having inconsistent download speeds across the country.
For Canada, the download speed is fairly uniform, according to a report from Opensignal. According to the wireless coverage mapper, such inconsistencies arise when the 4G networks are congested. Further, the congestion in the 4G networks slower than 5G.
But Canada’s 4G infrastructure is solid. This is to say that the rollout of the next level connection will not be a daunting task. In particular, 5G operates at spectrums with higher frequency and bandwidth. This is to say that users will not experience the congestions which are present in 4G. As such, the bandwidth will be more productive and more and more devices will be able to connect and utilize the internet better.
While Canada might be a step behind in the adoption of 5G, plans are in motion. In early 2019, wireless companies in Canada splashed $3.5 billion CAD to have a piece of the 600 megahertz frequencies band. By April 2019, operators had spent close to $17.6 billion during spectrum auctions to acquire the requisite resources.
- What is the future of 5G in Canada?
This band has a higher capability for penetrating buildings and can cover large swaths of geographical areas. Particularly, this is the broadband which should help to usher in a 5G era in the country. By 2021, Canada is expected to auction tow more sets of bands of higher frequencies to give enough room to operators to exploit 5G’s potential.
Between 2020 and 2026, Canadian firms should spend up to $26 billion in investments to acquire necessary infrastructure to rollout 5G, an Accenture report claims. Such big bets on the novel wireless connection are indicative of what 5G has to offer in terms of connectivity and revenue.
In June 2017, TELUS and Huawei collaborated on a pilot program aimed at test-running a live 5G network in Canada. According to the companies, the pilot was successful and it concluded that users will be able to experience 200x better speeds than the current 4G LTE connection.
According to the results, the pilot users will be able to operate smart homes with the help of Wireless-to-the-Premise (WTTx) connectivity. Further, businesses of tomorrow such as the ones involving IoT will run successfully and reliably.
The companies said they should be able to leverage the pilot to create the best 5G ecosystem in Canada. In particular, Huawei, through its Vancouver-based proxy, 5G Living Lab, and TELUS have been running research within the region for four years now.
The market size for 5G in Canada
There is a huge market for 5G and other faster technologies in Canada. This is depicted by the demand for wireless services and the uptick in the consumption of mobile data. According to CWTA, over 32.8 million or 88% of Canadians used wireless services in 2018. Of this number, over 12.35 million people relied on wireless services exclusively.
On the data consumption front, Canada is also strong. Notably, data traffic in 2017 expanded to 38%, according to CTWA. Between 2017 and 2022, this traffic was estimated to grow at 34% CAGR, which basically implies a four-fold grow within five years.
Interestingly, this massive growth in data consumption comes on the back of a robust connection speed under the 4G LTE infrastructure. As such, the possibility of these people pushing for a 5G rollout is huge.
In particular, the expanding market for faster wireless connectivity should expedite 5G adoption. In fact, Statista predicts that 5G connections as a share of mobile connections will be higher in 2025 than in 2021. By 2021, 5G will account for 8% of all mobile connections. This value should shoot to 49% in 2025.
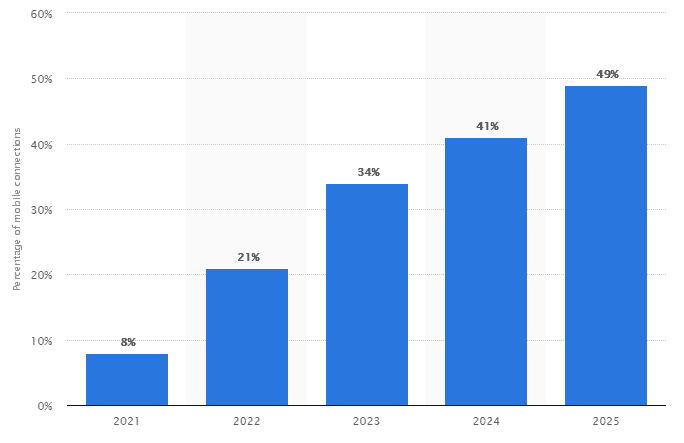
Source: Statista
The expected economic impact of 5G on Canada
5G is expected to have a massive impact on the economy in Canada. According to the Accenture report, adoption of this technology should add $40 billion CAD more to the country’s GDP annually. Notably, the technology will add value through stimulating innovation in Canadian industries.
Further, there will be more jobs created and Canadians quality of life will be improved. In particular, over 250,000 jobs will be created which are directly linked to 5G. As per the report, 7,053 direct jobs will be created in 2020 while 4,958 jobs will be created indirectly. In 2026, 13,831 jobs will result directly from 5G while an additional 9,704 will be created indirectly. Therefore, the jobs created will be incremental over the years.
Accenture further noted that the growth in jobs and GDP will be occasioned by increased competitiveness as a result of the adoption of 5G. Particularly, 5G should help Canadians to practice precision agriculture through smart irrigation and the use of sensors in the soil to monitor crops. Subsequently, farmers will be able to save $270 annually. Pervasive sensors should help in predictive maintenance and which should help to cut 20% of maintenance costs.
What should Canada do to expedite 5G adoption?
The first step that authorities in Canada should take is to expedite the allocation of spectrum. In particular, Canada should endeavor to free up as much spectrum as it possibly can so that the new technology should be able to go through the spectral adaptability phase successfully.
Secondly, authorities should update the regulations, fees, and rules which govern the telecommunications sector to reflect the new dynamics. For instance, 5G relies on new and revolutionary infrastructure compared to the massive towers used in legacy connections. Therefore, there is a need for across board modernization of infrastructure and administrative processes.


